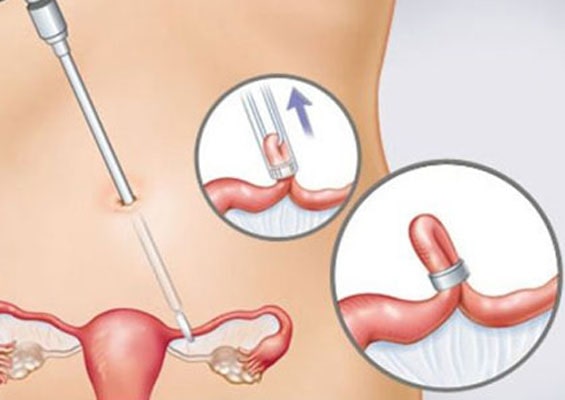
Sterilization/ Tubal ligation is a permanent method of contraception. This can be done via laparoscopy or laparotomy (open) method. Female sterilization involves obstruction or removal of the fallopian tubes.
The fallopian tubes are on either side of the uterus and extend toward the ovaries. They receive eggs from the ovaries and transport them to the uterus. Once the fallopian tubes are closed or removed, the man's sperm can no longer reach the egg.
Laparoscopy enables the physician to complete tubal ligation or tubal removal by making a small incision near the navel. This smaller incision reduces recovery time after surgery and the risk of complications. In most cases, the woman can leave the surgery facility on the same day of surgery and resume light daily routine from the next day itself.